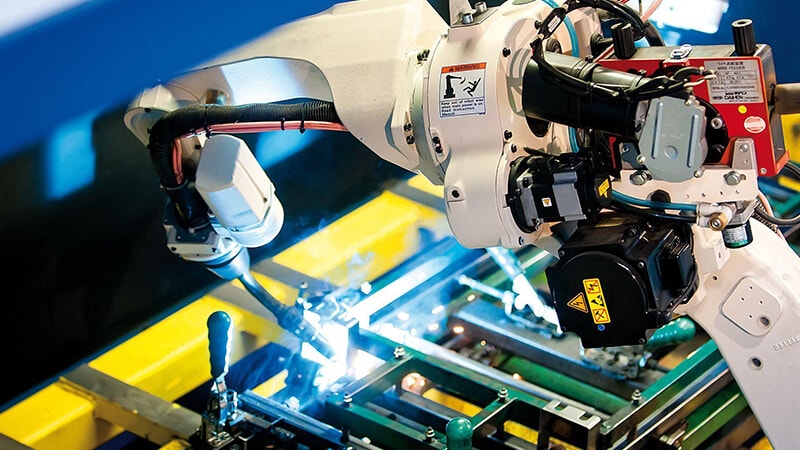
Robotic welding has really taken place in manufacturing companies.
By 2016 there were more than 250,000 welding robots around the world. The countries that use robotic welding the most are Japan, China and the United States of America, in that order.
But to get started with this topic, let’s define what is robotic welding.
What is robotic welding
To start, let’s define robotic welding. We can say that robotic welding is the use of mechanical tools capable of being programmed (robots) to perform welding processes in an automated way.
These processes should include both welding the pieces and moving them.
Using an example, let’s see how extensive robotic welding is. Of the approximately 120,000 robots in the United States by 2005, half were used for welding processes.
Ten years later, the trend is similar. This makes it clear that welding is by far the most used application by robotics.
When welding is robotic
When a human operator participates directly in the welding process, as sometimes happens with the GMAW, we cannot say that it is purely robotic welding.
If a human operator participates in operation with a robot, under established and controlled safety conditions, we are in the presence of a Collaborative System. These systems are called Collaborating Robots.
Now, spot welding and large-scale arc welding that is done in automobile manufacturing is in fact robotic welding.
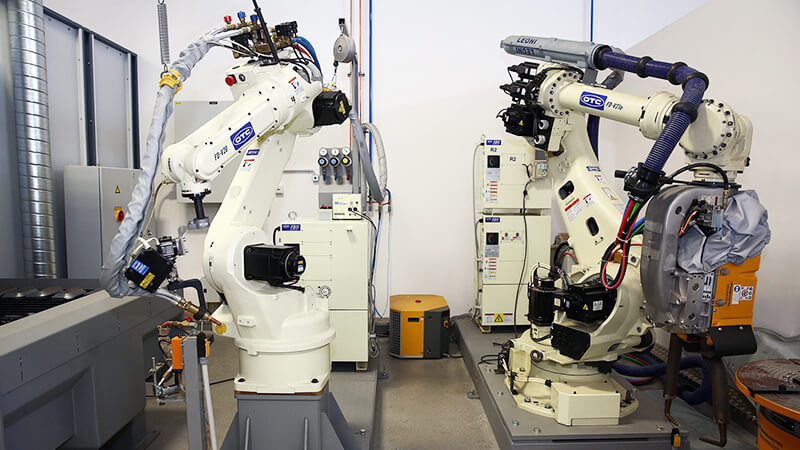

Who uses robotic welding
Welding robots have been used mainly by large manufacturing companies, with the automotive being the main one.
Secondly, we can include large to medium-sized companies that manufacture products or spare parts, again, for the automotive company.
Medium to small companies rarely or never would use welding robots in their processes.
It is evident that the costs that welding robots would use to have had a lot of weight for the company.
However, the trend is changing. As always, technology gets a lower price as is established in the market.
In addition, more diverse welding robot systems, including portable ones, have been created that meet more particular needs.
Today, both medium and small industries can use welding robots with only a small investment.
The origin of robotics in welding
In the United States, they started making robots in the 60s of the 20th century. However, its application to welding began about 20 years later.
At that time the automobile industry began to use spot welding to manufacture vehicles, for which it employed robots.
At first, the use of robotic welding was very basic, but given its effectiveness, it soon began to be applied for more processes.
Today, only robotic arc welding takes 20% of industrial automated welding applications.
Let's use the new technologies
Automation is the present and the future
Processes that can be done with robotic welding
With robotic welding, arc welding can now be done in GMAW, GTAW and Plasma, spot welding, sheave welding and laser welding.
The fact that robotic welding can be used for more processes or in different circumstances will motivate more companies to obtain some welding robots.
These improvements will only serve to increase the speed or quality with which they produce.
The shortage of operators
It is also true that it will be increasingly difficult to get operators who are properly trained for professional welding jobs.
The AWS (American Welding Society) has calculated that by 2020 there will be a shortage of 290,000 professional welders in the United States.
Similar scenarios can be expected in other countries.
On the other hand, the health and safety of operators is something that must also be taken into account.
When welding gases are emitted that are harmful to health. This issue will be explained later in this article.
Effectiveness and efficiency are also key factors whereby a company may need robotic welding.
In fact, they are essential to produce high-quality products and improve the price to the public.
Given these criteria, more and more companies should consider including robotic welding in their manufacturing processes.
When welding robots are necessary
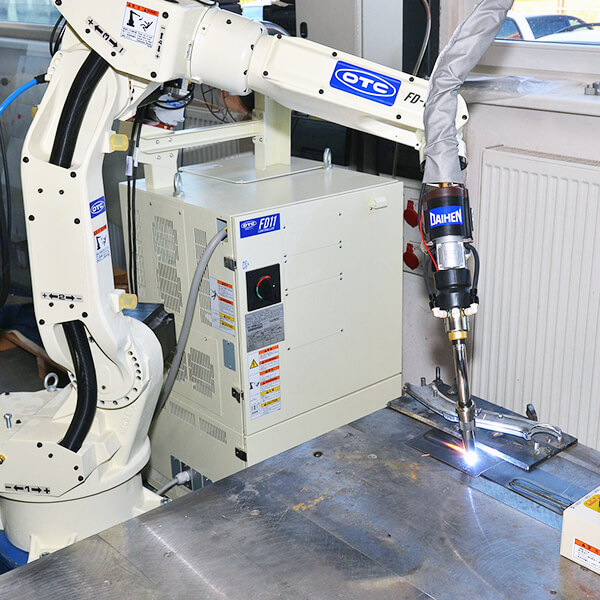

A company should consider the possibility of including welding robots in its processes if one or more of the following points identify its operation:
- They need to increase production
- They need to reduce operating costs
- There are jobs for which they don’t get staff
- They need to improve the quality
- They need to complete jobs consistently
- Some jobs are very difficult to do manually
- Some jobs are or can be dangerous or polluting for operators
With respect to these points, reducing operating costs is something constant in all companies, no matter where they are.
So all of them should use welding robots to improve their costs in the medium and long term.
Equipment for robotic welding
When the matter about the equipment necessary for robotic welding is brought out, it immediately comes to the minds of those responsible in companies that are very expensive machines.
Although some are still expensive today, as has happened with computers and personal devices, technologies have dropped out the price over time.
This has made it possible for smaller companies to have been able to obtain robotic welding equipment and are benefiting from having reduced their costs.

This trend, known as the “Moore’s Law” will continue. It is expected that manufacturers produce new models more specialized and at a lower price.
Another common idea is that they are very specialized equipment and it will be very difficult or unpayable to have trained personnel to handle it.
But in fact, welding robots are not usually that complex. The training required for the operation of a robot is divided into 2 parts.
A part of the training is for the operator who loads and unloads the material to be welded. Only a few minutes of training may be necessary.
The other part is the robot programmer training. This will take between a few hours or a few days depending on your welding experience and whether or not you will use virtual programming software.
Ideally, the person in charge should have knowledge of welding processes, in order to confirm that the job has been well done.
It is also ideal that this person knows or has some idea of how to run a program. So logical thinking is ideal for this type of work.
Most robotic welding systems have several aspects in common, regardless of the application for which they will be used.
So, someone who has been trained to program a welding robot most likely will be able to handle a different one in a short time.
Parts of a welding robot
Basically a welding robot is composed of 3 main parts and some other secondary parts.
The main part is a manipulator or “arm.”
This is the part of the machine that repeats movements with high precision in their respective 6 to 7 axes to bring the torch to a position to execute the welding.
The second component is the controller. This coordinates the movements of the axes of the arm and is the central computer of the system.
Some have PLC capabilities included being able to coordinate many alternate tasks to the robot’s movement.
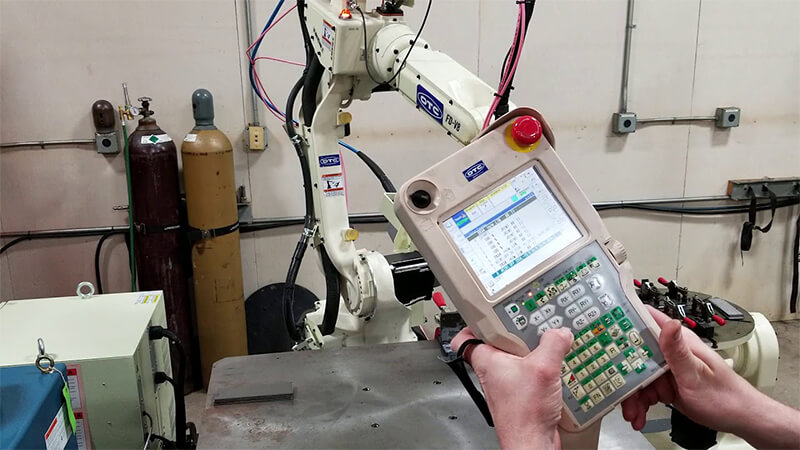
The operator sends instructions to the controller through a program that he creates in the command/teaching panel (also known as Teach Pendant).
The third basic component is the welding power source. It receives a configuration from the controller for each welding bead that the manipulator or “arm” performs.
Some of the other common parts in welding robots are
- Sensors
- Cables
- Communication devices
- Interfaces
- Nozzle cleaners with wire cutters
- Positioning systems such as horizontal or vertical two-axis rotators
These positioners allow the piece to be adjusted in the best possible welding position.
The positioners can become medium or large structures that help improve the productivity of the robot and the operators for loading and unloading materials to be welded.
Choose the welding robot from the best brand
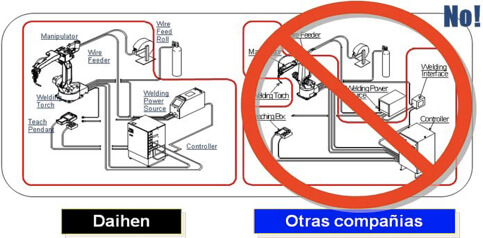
Although there are several brands that produce welding robots, we have proven that the ones from OTC Daihen are the best value on the field.
The companies that have implemented them have benefited from the total integration in a single native language of all its components (Manipulator, Control, Welding Source, and Positioners)
This has allowed the easiest programming of the robot in the arc welding processes of the market.
We have successfully installed several of the welding robot models of the OTC Daihen to different clients in South America.
In the video, you can see this one of these robots in action.
Of course, each manufacturing plant has its own needs and, based on that, we recommend which welding robot would be appropriate.
In any case, we invite you to contact us for advice.
The human side of automation
It is almost impossible, when it comes to automation in the company, that operators do not feel fear for their jobs.
It is common for some to feel contempt, and even try to sabotage the implementation of robotic welding in the company, in order to avoid losing their jobs.
However, the vast majority of companies that implement automated welding in their processes do not do so to fire personnel, but to expand their production.
Often the staff is transferred to other areas where their capabilities can be used.
In fact, automation generates new jobs, because, in every place where there is a welding robot, someone will need to program and control it.
But this factor is not evident for most operators. That is why they have a negative perspective.
For companies that are going to take the step to automation, they are recommended to provide information to their staff.
For many, it is important to know that a machine is not going to take away their job.
Perhaps the opportunity can be taken to promote productivity among plant personnel.
About the health of the operators
It is evident that increasing productivity through welding robots will also increase the number of gases emitted during operation.
This increase in pollution can be prevented from affecting the health of employees by placing smoke extraction systems near the cells of welding robots.
Of course, the company that provides robotic welding equipment must be able to help you plan these matters.
When we install automated welding in a plant, we previously visited it to know its current situation and what they want to achieve.
This allows us to design a tailored solution that meets their needs.
The clamping device (JIG)
In most robot welding applications, the clamping device is considered the most important component for a successful implementation.
This auxiliary equipment receives the parts to be welded from the operator and adjusts them with high precision to ensure a position in the three coordinates consistently.
In this way, the welding robot will be able to accurately make the same welding bead from start and end, welding after welding.
The characteristics of the parts to be placed in the clamping device (JIG) must always be the same.
The length, height, thicknesses, angles, arcs, folds and other geometries must always be consistent to ensure that the JIG positions the set of parts to be welded correctly.
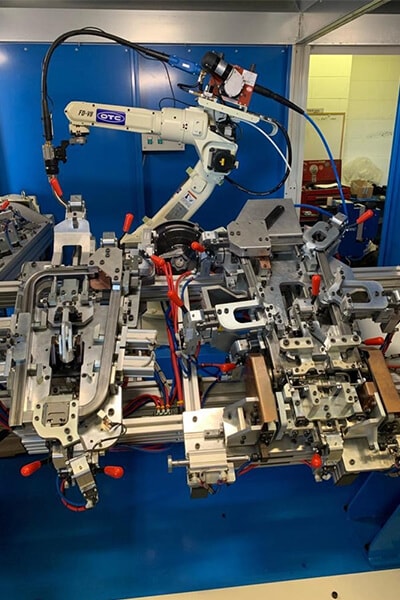
To successfully develop the clamping device (JIG) companies have 2 options: If they have an engineering department, they can design the shape and mechanism of this component.
Otherwise, the supplier of the welding robot, like our company, can provide the JIGS design and manufacturing service, according to the client’s application.
How to implement robotic welding in your company
Implementing automated welding processes in the company is not an activity that is done in one day.
On the contrary, even in plants where welding is an integral part of production processes, this change to automation can take up to a year.
The key to implementing robotic welding successfully in the company is to keep it as simple as possible and that this covers all or most of the repetitive processes of the operation.
To explain it better: Suppose that a production line is divided into 4 sections, of which 1 is very complicated and requires custom welding while the other 3 are constant and unchanged processes.
The section that can vary, due to the welding that must be customized can be done by an operator.
The other 3 sections, composed of repetitive processes, can be perfectly completed by a welding robot.
The welding performed by the robot is indicated through a program. To improve the efficiency of the robot, the idea is to run the same program for a long period of time, instead of constantly changing the program.
Some companies even prefer that a welding robot perform a single program and obtain another that performs another operation. That way they never stop them.
Another issue to take into account is the number of movements that the robot must make and the heat that the welding produces in the piece.
The welding robot operator
The ideal person to handle the robot must be someone who knows how to weld and has knowledge of how to program any CNC type machine.
Even if it is not going to program in G code, experience gives you the notion of step-by-step programming logic of welding operations.
Whether or not it has been a welding operator is important when it comes to seeing problems that have been caused in the parts welded by the robot.
If this person has no idea of welding, he will not know what the problem may be.
An expert welder, meanwhile, seeing a wrong result of a welded part, can determine which of the many factors that may be affecting the robot.
However, the skilled welder may also have the tendency to always do manual welding and not use a machine that replaces his work.
This makes it a challenge for the company to find the right person to do this job.
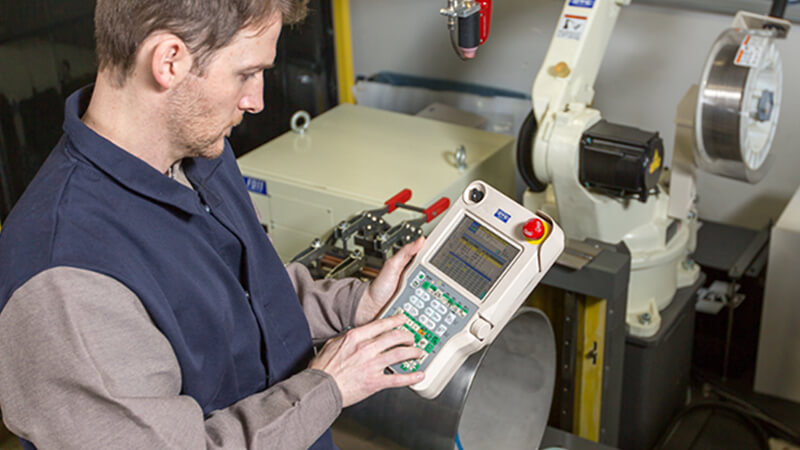

Having notions of how a device can be programmed to perform an action is of course very useful as well.
However, most of the time this particular training is provided by the company that advises and sells robotic welding equipment.
One of the most important skills that the selected person must have is the ability to remain focused, see details and recognize patterns.
For example, if one of the pieces was not well welded, even a small detail, it could be because it was not well placed in the position where it should go.
But if the next one is also bad, it may be something else.
In cases like these it is better to momentarily stop the operation and correct the error.
Finally, the designated operator must also be able to carry out a preventive maintenance program for the welding robot.
This will help prevent major arrests and expenses for unforeseen repairs.
Robot welding has many advantages
If well implemented, robotic welding can exponentially increase the productive capacity of any company.
This could mean a greater quantity of products for sale, with possibly the same number of personnel.
Although there is no standard, the return on investment by a welding robot is usually 12 to 15 months.
But the life of robotic welding equipment is much longer. This could increase the company’s income or lower product prices.
So, in general, robotic welding leads companies to be more competitive, cover more markets and improve their revenues. More than enough reasons to implement it in your company.
We want and can help you define what is the robotic welding equipment you need for your operation. Contact us at any time to receive more information.
Did you like this article? We invite you to comment. Do you have questions? Contact us or ask them in the comments section and very soon we will be answering.